Integrity verification in background
Description¶
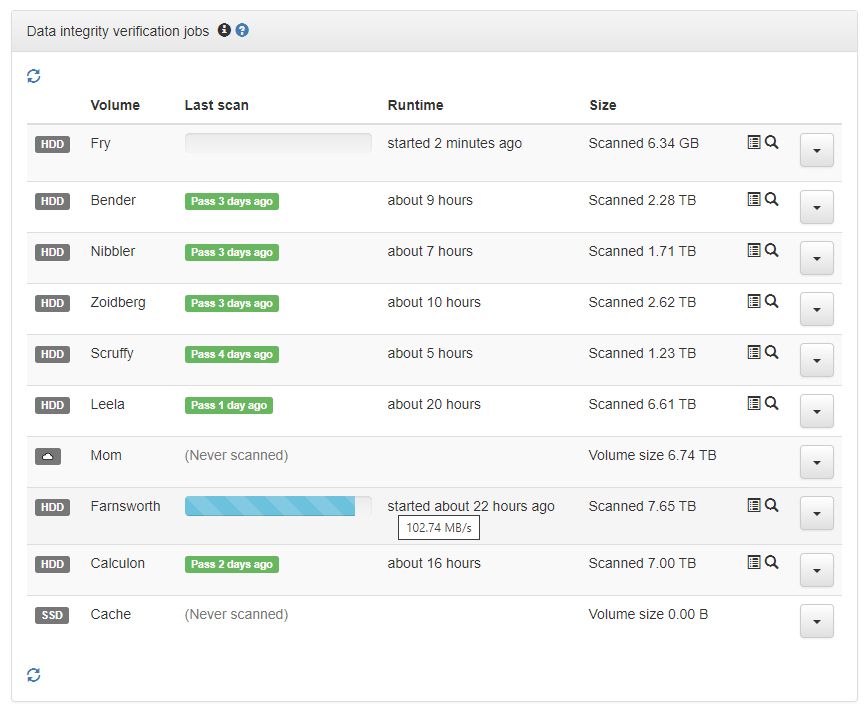
In addition to verifying content hashes on file reads "in realtime", we also have background jobs for verifying integrity of entire volumes' files - also known as "scrubbing".
Varasto can scan through your volumes to verify that all the replicas are healthy, and raise an alert if any bit rot or I/O errors are detected.
Which errors can we detect?¶
Traditionally, filesystems without content integrity verification have trusted on the hard drive to report I/O errors and bit rot. That's a risky strategy because hard drives can lie.
We use Content-Addressable Storage to detect errors even if the hard drive would try to lie to us, so errors won't go undetected:
| Error type | Detected by OS | Detected by Varasto |
|---|---|---|
| Drive reports I/O error | ☑️ | ☑️ |
| Drive reports bit rot error | ☑️ | ☑️ |
| Drive lies about bit rot or I/O error | ☐ | ☑️ |
| An attacker tampers with your file | ☐ | ☑️ |
Pause / resume¶
These scans can be very long operations, when you have terabytes of data to plow through. You can pause/resume scans if you need release some throughput or restart Varasto server or the computer. Scanning jobs are also resilient to crashes - no need to start all over.
TODO
We should support running the scanning operation with a lower I/O priority so the scans have the least chance of disturbing anything.
Scheduling¶
TODO
We only support manually starting these scanning jobs - no automatic scheduling of them yet.
What if I encounter an error?¶
If your data has silently corrupted on-disk, or if the disk gives I/O errors, the safest option is to remove the drive and replace it with a new one. We have instructions for this.
If you're unwilling to spend money, you can try to find out how serious the problem is and if there's some hope, keep using it at your own risk - but please keep enough replicas, follow the SMART diagnostics and prepare for the drive failing.
How does this work with encryption?¶
We have tricks to enable integrity verification without having access to the encryption keys. Read more in encryption documentation.